The data in a SSTable is organized in six types of component files. The format of a SSTable component file is
<keyspace>-<column family>-[tmp marker]-<version>-<generation>-<component>.db
<keyspace> and <column family> fields represent the Keyspace and column family of the SSTable, <version> is an alphabetic string which represents SSTable storage format version, <generation> is an index number which is incremented every time a new SSTable is created for a column family and <component> represents the type of information stored in the file. The optional "tmp" marker in the file name indicates that the file is still being created. The six SSTable components are Data, Index, Filter, Summary, CompressionInfo and Statistics.
For example, I created a column family data in Keyspace usertable using cassandra-cli and inserted 1000 rows {user0, user1,...user999} with Cassandra version 1.2.5.
create keyspace usertable with placement_strategy = 'org.apache.cassandra.locator.SimpleStrategy' and strategy_options = {replication_factor:1};
use usertable;
create column family data with comparator=UTF8Type;
The SSTables under cassandra/data/usertable/data directory:
usertable-data-ic-1-CompressionInfo.db
usertable-data-ic-1-Data.db
usertable-data-ic-1-Filter.db
usertable-data-ic-1-Index.db
usertable-data-ic-1-Statistics.db
usertable-data-ic-1-Summary.db
usertable-data-ic-1-TOC.txt
In the above SSTable listing, the SSTable storage format version is ic, generation number is 1. The usertable-data-ic-1-TOC.txt contains the list of components for the SSTable.
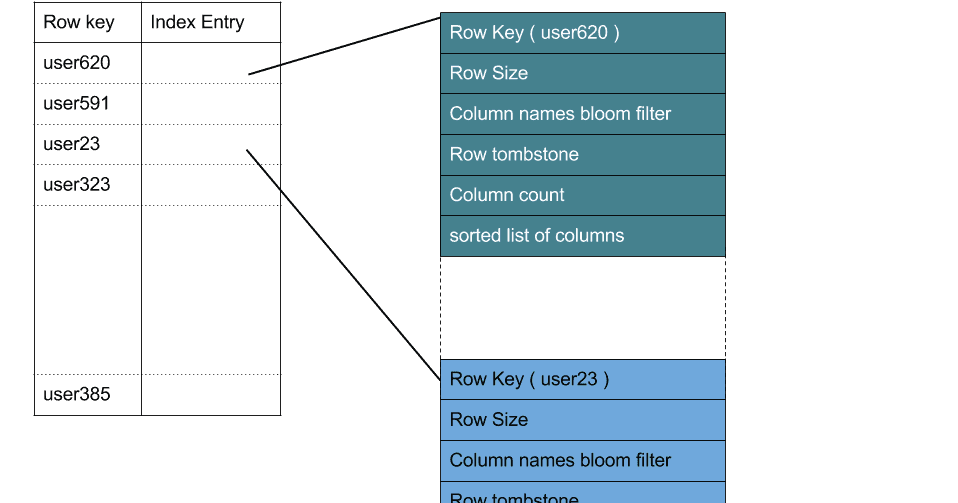
Data file stores the base data of SSTable which contains the set of rows and their columns. For each row, it stores the row key, data size, column names bloom filter, columns index, row level tombstone information, column count, and the list of columns. The columns are stored in sorted order by their names. Filter file stores the row keys bloom filter.
Index file contains the SSTable Index which maps row keys to their respective offsets in the Data file. Row keys are stored in sorted order based on their tokens. Each row key is associated with an index entry which includes the position in the Data file where its data is stored. New versions of SSTable (version "ia" and above), promoted additional row level information from Data file to the index entry to improve performance for wide rows. A row's columns index, and its tombstone information are also included in its index entry. SSTable version "ic" also stores column names bloom filter in the index entry.
Summary file contains the index summary and index boundaries of the SSTable index. The index summary is calculated from SSTable index. It samples row indexes that are index_interval (Default index_interval is 128)apart with their respective positions in the index file. Index boundaries include the start and end row keys in the SSTable index.
All SSTable storage format versions and their respective Cassandra versions are described in https://github.com/apache/cassandra/blob/trunk/src/java/org/apache/cassandra/io/sstable/Descriptor.java and the different components are described in https://github.com/apache/cassandra/blob/trunk/src/java/org/apache/cassandra/io/sstable/Component.java
SSTable data format (version "jb")
A column inside a row is stored as four parts. It begins with column name, followed by the type of the column, its creation time and column value. A column name is stored as two bytes indicating the length of the name followed by the name itself. The type is a one byte mask value indicating the type of stored column. Based on the column type remaining bytes of the column are processed.
Column timestamp is a eight bytes value indicating the column creation time. For a deleted column, the timestamp indicated the time when the column was deleted. Column value is stored as four bytes indicating the value size followed by the bytes storing the actual column value.
Version "ja"
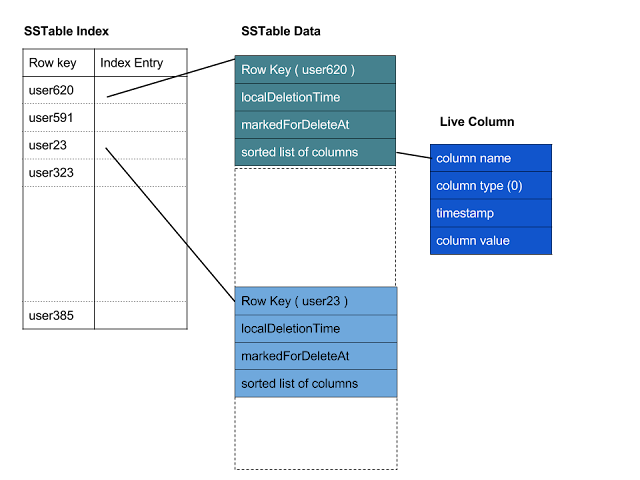
In version "ja" SSTable format, Column names bloom filter, Column count fields are removed from SSTable data component file. The fields, localDeletionTime and markedForDeleteAt added to represent deletion timestamps of a row. For a row tombstone, localDeletionTime represents the timestamp in seconds at which a top level tombstone is created and markedForDeleteAt represents a timestamp in microseconds after which the data in a row should be considered as deleted. The default value for localDeletionTime is 0x7fffffff and the default value for markedForDeleteAt is 0x8000000000000000. If a row's deletion timestamps contain the default values then it contains live data.
Row size field is also removed from data component file. A special 0 length column name is added to represent the end of row. Row size is calculated from Index file. Index file contains starting offsets of each row. Successive offsets are used to calculate each row size except for the last row in SSTable. For the last row, end of data file is used to calculate its size.
Version "ka"
In version "ka", contents of Statistics component file is split in to 3 types of metadata called validation, compaction and stats. Validation metadata is used to validate SSTable which includes partitioner and bloom filter fp chance fields. Compaction metadata includes ancestors information which is also available in older formats and a new field called cardinality estimator. Cardinality estimator is used to efficiently pre-allocate bloom filter space in a merged compaction file by estimating how much the input SStables overlap. Stats metadata contains rest of the information available in old formats and two additional fields. First one is a flag to track the presence of local/remote counter shards and the other one is for storing the repair time.
sstable2json.py
sstable2json.py reads the rows and columns in a given SSTable and converts those to JSON format similar to sstable2json tool available in Cassandra distribution. It doesn't require access to Cassandra column families in system keyspace to decode SSTable data like sstable2json tool. It is tested with version "jb".